A “potentially hazardous” asteroid the dimensions of a skyscraper is set to zip previous Earth on Tuesday (Sept. 17), according to NASA.
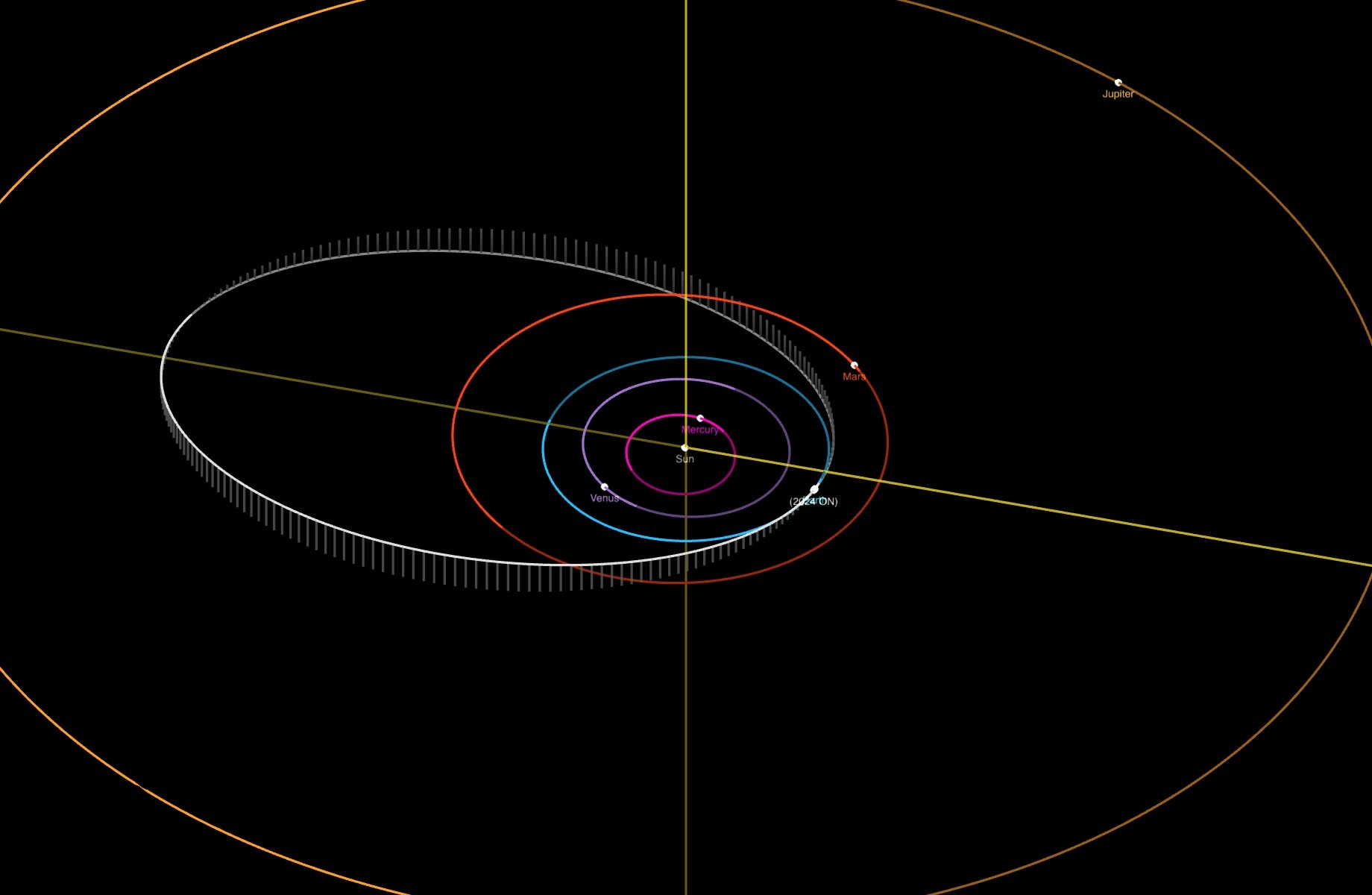
The skyscraper-size asteroid, named 2024 ON, has an estimated diameter between 721 and 1,575 ft (220 to 480 meters), and will zip previous the Earth at 19,842 mph (31933 km/h) — or round 26 instances the pace of sound.
At its closest strategy, the asteroid will come inside about 0.62 million miles (1 million kilometers) of Earth, round 2.6 instances the typical distance between Earth and the moon. By cosmic requirements, this is an extremely tight margin — however nonetheless far sufficient away that no Earthlings want fear concerning the passing house rock.
NASA deems any house object that comes inside 120 million miles (193 million km) of Earth a “near-Earth object” and classifies any giant object inside 4.65 million miles (7.5 million km) of our planet as “potentially hazardous.” NASA tracks the areas and orbits of roughly 28,000 asteroids, following them with the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS), an array of 4 telescopes that carry out a scan of the complete night time sky each 24 hours.
NASA has estimated the trajectories of all these near-Earth objects past the top of the century. Earth faces no identified hazard from an apocalyptic asteroid collision for at the very least the following 100 years, in response to NASA.
Related: Why are asteroids and comets such bizarre shapes?
If 2024 ON had been to hit Earth, it will not trigger a cataclysmic occasion just like the 7.5-mile-wide (12 km) dinosaur-killing asteroid that struck Earth 66 million years in the past. But this doesn't suggest its results would not be far-reaching. For instance, a 2013 explosion of a 59-foot-wide (18 m) meteor above Chelyabinsk, Russia, generated a blast roughly equal to round 400 to 500 kilotons of TNT, or 26 to 33 instances the vitality launched by the Hiroshima bomb, and injured round 1,500 individuals.

Understanding the trajectories of asteroids may be a tougher activity than it first seems due to the so-called Yarkovsky impact. Named after the Nineteenth-century engineer who first proposed it, the impact implies that, over lengthy durations of time, house rocks take in and emit sufficient momentum-carrying mild to subtly change their orbits. This implies that quantifying the Yarkovsky impact is essential when predicting which asteroids are potential threats.
Space companies world wide are already engaged on attainable methods to deflect a harmful asteroid if one ever headed our means. On Sept. 26, 2022, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft redirected the non-hazardous asteroid Dimorphos by ramming it off target, altering the asteroid's orbit by 32 minutes within the first check of Earth's planetary protection system. NASA has since hailed the mission as a success past all expectations.
China has additionally stated it is within the early planning phases of an asteroid-redirect mission. By slamming 23 Long March 5 rockets into the asteroid Bennu, which will swing inside 4.6 million miles (7.4 million km) of Earth's orbit between the years 2175 and 2199, scientists hope to divert the house rock even farther from its present trajectory..
For these fascinated about following the course of 2024 ON because it skims previous our planet, the Virtual Telescope Project will present a live feed of its path beginning on Sept. 15 at 19:30 UTC, when the thing will be seen within the Northern Hemisphere.

